WHAT IS ECU?
WHAT IS ECU?
An Engine Control Unit, or ECU, is a computerized device
that controls various engine functions in a vehicle. It is responsible for
monitoring and adjusting various engine parameters such as fuel injection,
ignition timing, and valve timing to optimize performance and reduce emissions.
The ECU receives input from various sensors throughout the
engine and uses this information to adjust the engine's performance in
real-time. For example, if the sensor detects that the engine is running too
hot, the ECU will adjust the air-fuel ratio to cool it down.
ECU's are also responsible for controlling other functions
such as the transmission, ABS, and air conditioning systems. They use complex
algorithms and lookup tables to make decisions about how to control these
systems based on the input from various sensors.
ECU's have become increasingly sophisticated over the years,
with many now featuring hardware and software that allow for reprogramming and
tuning. This allows mechanics and car enthusiasts to adjust the vehicle's
performance to suit their needs, whether that be for improved fuel efficiency,
increased horsepower, or better emissions.
Overall, the Engine Control Unit is a crucial component of a
vehicle's powertrain, responsible for ensuring optimal performance, fuel
efficiency, and emissions.
There are several types of Engine Control Units (ECUs) used
in vehicles, each with a specific function. Some of the most common types
include:
1)Powertrain Control Module (PCM) - This is the main ECU
that controls the engine and transmission. It receives input from various
sensors and uses this information to adjust the engine's performance in
real-time.
2)Engine Control Module (ECM) - This ECU is specifically
responsible for controlling the engine. It monitors and adjusts various engine
parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve timing to
optimize performance and reduce emissions.
3)Transmission Control Module (TCM) - This ECU controls the
transmission. It monitors the transmission's speed, temperature, and gears, and
adjust the transmission's performance accordingly.
4)Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) Control Module - This ECU
controls the ABS system. It monitors the vehicle's speed and braking conditions
and adjust the braking system to prevent wheel lockup.
5)Body Control Module (BCM) - This ECU controls various body
systems such as lighting, windows, door locks, and mirrors.
6)Airbag Control Module - This ECU controls the airbag
system. It monitors the vehicle's speed and collision conditions, and deploys
the airbags if necessary.
7)Traction Control Module - This ECU controls the traction
control system. It monitors the vehicle's wheels to detect and correct any loss
of traction.
8)Electronic Stability Control (ESC) - This ECU controls the
stability control system. It monitors the vehicle's speed and direction, and adjusts
the brakes and engine to keep the vehicle stable.
It's worth noting that different vehicle manufacturers might
use different names for their ECU and the specific function of an ECU may vary
depending on the make and model of the vehicle.
image credit: clearmechanic.com
1) Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is the main Engine
Control Unit (ECU) that controls the engine and transmission of a vehicle. It
receives input from various sensors throughout the engine and transmission, and
uses this information to adjust the engine's performance in real-time.
The PCM is responsible for monitoring and adjusting various
engine parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve timing to
optimize performance and reduce emissions. It also controls the transmission,
including the gear selection and shifting patterns.
The PCM uses complex algorithms and lookup tables to make
decisions about how to control the engine and transmission based on the input
from various sensors. For example, if the engine is running too hot, the PCM
will adjust the air-fuel ratio to cool it down. If the transmission is getting
too hot, the PCM will adjust the shifting pattern to reduce heat.
The PCM also communicates with other systems in the vehicle
such as the anti-lock braking system (ABS) and the traction control system
(TCS). It uses information from these systems to adjust the engine and
transmission to improve vehicle stability and safety.
In addition, PCM allows for reprogramming and tuning to
adjust the vehicle's performance to suit the driver's needs, whether that be
for improved fuel efficiency, increased horsepower, or better emissions.
Overall, the Powertrain Control Module is a crucial
component of a vehicle's powertrain, responsible for ensuring optimal
performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
2)The Engine Control Module (ECM) is an Engine Control Unit (ECU) that is specifically responsible for controlling the engine of a vehicle. It receives input from various sensors throughout the engine and uses this information to adjust the engine's performance in real-time.
The ECM is responsible for monitoring and adjusting various
engine parameters such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve timing to
optimize performance and reduce emissions. It also controls other
engine-related functions such as the engine idle speed, the exhaust gas
recirculation system, and the evaporative emission control system.
The ECM uses complex algorithms and lookup tables to make
decisions about how to control the engine based on the input from various
sensors. For example, if the sensor detects that the engine is running too hot,
the ECM will adjust the air-fuel ratio to cool it down.
The ECM also communicates with other systems in the vehicle
such as the powertrain control module (PCM) and the transmission control module
(TCM). It uses information from these systems to adjust the engine to improve
vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
In addition, ECM allows for reprogramming and tuning to
adjust the vehicle's performance to suit the driver's needs, whether that be
for improved fuel efficiency, increased horsepower, or better emissions.
3. The Transmission Control Module (TCM) is an Engine
Control Unit (ECU) that controls the transmission of a vehicle. It receives
input from various sensors throughout the transmission and uses this
information to adjust the transmission's performance in real-time.
The TCM is responsible for monitoring and adjusting various
transmission parameters such as gear selection, shifting patterns, and torque
converter lockup to optimize performance and improve fuel efficiency. It also
controls the transmission's cooling system, and it monitors the transmission's
speed, temperature, and gears, and adjust the transmission's performance
accordingly.
The TCM uses complex algorithms and lookup tables to make
decisions about how to control the transmission based on the input from various
sensors. For example, if the transmission is getting too hot, the TCM will
adjust the shifting pattern to reduce heat.
The TCM also communicates with other systems in the vehicle
such as the engine control module (ECM) and the powertrain control module
(PCM). It uses information from these systems to adjust the transmission to
improve vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
In addition, TCM allows for reprogramming and tuning to
adjust the vehicle's transmission performance to suit the driver's needs,
whether that be for improved fuel efficiency, increased torque or better
shifting patterns.
Overall, the Transmission Control Module is a crucial
component of a vehicle's powertrain, responsible for ensuring optimal
performance, fuel efficiency and safety of the transmission system.
4)The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) Control Module is a
computerized device that is responsible for controlling the operation of the
ABS system in a vehicle. The primary function of the ABS system is to prevent
the wheels from locking up during heavy braking, which can cause the vehicle to
skid and lose control.
The ABS Control Module receives input from various sensors
located on the vehicle, such as wheel speed sensors, brake pedal position
sensor and yaw rate sensor. It then uses this information to determine if a
wheel is about to lock up, and if so, it sends a signal to the brake system to
modulate the brake pressure at that wheel. This allows the driver to maintain
steering control and stability of the vehicle while braking.
The ABS Control Module also communicates with other vehicle
systems such as Engine Control Unit (ECU) and the electronic stability control
(ESC) to ensure that the ABS system is working in conjunction with other
systems for optimal performance.
In summary, The ABS Control Module uses input from sensors
to monitor the vehicle's braking system, and makes real-time adjustments to the
brake pressure at each wheel to prevent wheel lock-up, helping the driver to
maintain steering control and stability during heavy braking.
5)The Body Control Module (BCM) is a computerized device that
is responsible for controlling various functions in the body of a vehicle, such
as lights, windows, and doors. It is connected to various sensors and switches
throughout the vehicle, and uses this input to control the corresponding
outputs.
The BCM is responsible for controlling the following functions:
Lighting: The BCM controls the headlights, taillights, brake
lights, and turn signals. It also controls the interior lighting such as the
dome light and the instrument panel lights.
Windows: The BCM controls the operation of the power
windows, including the up and down movement, as well as the express-up and
express-down features.
Doors: The BCM controls the door locks, including the power
lock and unlock features, as well as the courtesy lights.
Wipers: The BCM controls the operation of the windshield
wipers, including the speed and interval settings.
Security: The BCM may also be responsible for controlling
the vehicle's security system, such as the alarm and remote keyless entry.
Climate Control: The BCM can control the settings of the
climate control system, such as the temperature, fan speed and direction, and
the mode of the air conditioning.
The BCM also communicates with other vehicle systems, such
as Engine Control Unit (ECU) and the ABS Control Module, to ensure that all
systems are working together for optimal performance.
In summary, the BCM is a computerized device that is
responsible for controlling various functions in the body of a vehicle, such as
lights, windows, and doors. It receives input from various sensors and switches
throughout the vehicle and uses this input to control the corresponding
outputs, and it also communicates with other systems to ensure that all systems
are working together for optimal performance.
6)The Airbag Control Module, also known as the SRS
(Supplemental Restraint System) Control Module, is a computerized device that
is responsible for controlling the deployment of airbags in a vehicle. It is
connected to various sensors throughout the vehicle, such as impact sensors and
seat belt tension sensors, and uses this input to determine when to deploy the
airbags.
The Airbag Control Module receives input from the impact
sensors located on the vehicle, such as those located in the front, sides, and
rear of the vehicle. These sensors measure the severity of an impact and send a
signal to the Airbag Control Module, which then determines if the airbags
should be deployed. The module also receives input from seat belt tension
sensors, which detect if the seat belt is being worn and if the seat is
occupied.
The Airbag Control Module also communicates with other
vehicle systems, such as the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and the ABS Control
Module, to ensure that all systems are working together for optimal performance.
The Airbag Control Module also has the ability to store
diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) in case of a malfunction, which can be read by
a mechanic with the use of diagnostic tool to identify the issue.
In summary, the Airbag Control Module is a computerized
device that controls the deployment of airbags in a vehicle. It receives input
from various sensors throughout the vehicle, such as impact sensors and seat
belt tension sensors, and uses this input to determine when to deploy the
airbags. It also communicates with other vehicle systems to ensure that all
systems are working together for optimal performance and it also has the
ability to store diagnostic trouble codes in case of a malfunction.
7)The Traction Control Module (TCM) is a computerized device that is responsible for controlling the traction of a vehicle. It is designed to help the driver maintain control of the vehicle by preventing the wheels from spinning excessively, especially on slippery surfaces such as ice, snow, or wet pavement.
The TCM receives input from various sensors such as the
wheels speed sensors and the brake pedal position sensor, and uses this
information to determine if a wheel is spinning excessively. When the TCM
detects excessive wheel spin, it will take action to reduce power to the
wheel(s) and/or apply the brakes to the slipping wheel(s) to regain traction.
It also works in conjunction with the Engine Control Unit
(ECU) and the Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) control module to ensure that the
engine power and brakes are being used optimally to maintain traction.
The TCM also communicates with other vehicle systems such as
the electronic stability control (ESC) to ensure that all systems are working
together for optimal performance.
In summary, the Traction Control Module (TCM) is a
computerized device that is responsible for controlling the traction of a
vehicle. It receives input from various sensors such as the wheels speed
sensors and the brake pedal position sensor, and uses this information to
determine if a wheel is spinning excessively. It then takes action to reduce power
to the wheel(s) and/or apply the brakes to regain traction and it also
communicates with other systems to ensure that all systems are working together
for optimal performance.
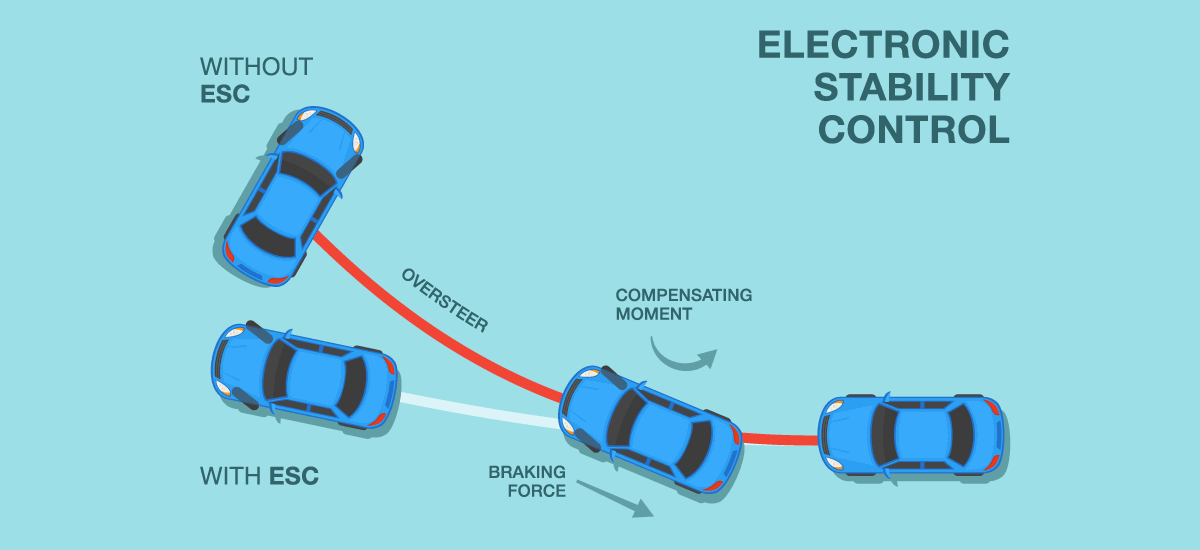
The ESC system uses various sensors such as the steering
wheel angle sensor, yaw rate sensor, and wheel speed sensors to measure the
vehicle's movement and compare it to the driver's intended direction of travel.
When the system detects a discrepancy between the two, it will take action to
correct the vehicle's path.
The ESC system uses a variety of techniques to regain
stability, such as braking individual wheels or reducing engine power. It can
also communicate with the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and the Traction Control
Module (TCM) to ensure that the engine power and brakes are being used
optimally to maintain stability.
When the ESC system detects an imminent loss of control, it
will activate a warning light on the dashboard, and in some cases, it will also
make an audible warning sound.
Modern vehicles have also integrated stability control
systems with additional features such as:
-Rollover Prevention: it detects when the vehicle is about
to roll over and take action to prevent it
-Trailer Stability Assist: it detect a trailer swaying and
take action to prevent it.
In summary, Electronic Stability Control (ESC) is a computerized
system that is designed to enhance the stability and control of a vehicle. It
uses various sensors such as the steering wheel angle sensor, yaw rate sensor,
and wheel speed sensors to measure the vehicle's movement and compare it to the
driver's intended direction of travel. When the system detects a discrepancy
between the two, it will take action to correct the vehicle's path, and it can
also communicate with other systems to ensure that the engine power and brakes
are being used optimally to maintain stability.





Comments
Post a Comment
if you have any doubts, pls let me know in the comment section .